ERMI Testing
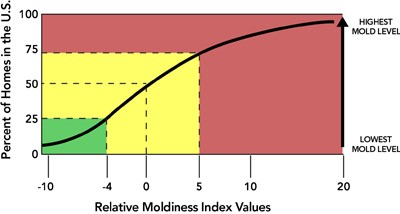
The Environmental Relative Moldiness Index (ERMI) was developed by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development (ORD) as a research tool to investigate mold contamination in homes. The methodology is based on using mold-specific quantitative polymerase chain reaction (MSQPCR) to quantify 36 molds and calculate an index number for comparison with a database of reference homes. According to the EPA, up to 50% of homes and workplaces in the US have past or current water damage.
What Are The Advantages of ERMI Testing?
The ERMI test offers several advantages over traditional mold screening methods. Dust in the home acts as a natural reservoir for mold spores and is more representative of mold levels over time versus short-term air samples. The ERMI test also has the benefit of more accurately detecting the presence of water damage indicator molds like Stachybotrys (Black Mold) and Chaetomium, which have a known potential to produce mycotoxins. Unfortunately, these types of molds are rarely detected with air samples due to their “wet” nature and heavy spores that seldom make it into the air in sufficient quantities to be sampled. Unfortunately again, these are the most dangerous molds to occupant health. If there is no visible mold to sample with a swab or tape lift, the ERMI is the only test capable of determining their presence.
When Should I Use the ERMI Test?
The ERMI test can be used for evaluating "moldiness" in indoor environments. Molds are found in every home but not all molds are always present. The ERMI helps to make an assessment if a home is more or less likely to have "unhealthy" mold conditions. Occupants sensitive to mold should especially consider using the ERMI to evaluate their indoor environment. Also, home buyers can use this tool to predict if their new home is likely to have a history of water damage or other environmental conditions conducive to mold development.
Contact Us Today For Investigation & Mold Testing In Charleston & The Surrounding Areas!